Outcomes, Complication Rates, and Stem Cell Procedures
Given the quite reasonable concerns this past week over the blinding of three women by a stem cell clinic injecting fat stem cells into eyes, I thought it was time to take a look at stem-cell-procedure complications. All medical procedures have complications. So what bar can we use to see if those complications are reasonable, and how should those be reported and measured?
Every Procedure Has Complications, and Every Medication Has Side Effects
First, to decide what complications might be reasonable, we need to understand the playing field of common side effects of conventional treatments. So what are some common complications in my world of orthopedic care, and how often do they happen?
- Knee replacement: The serious complication rates for this procedure are 8–16% (J Arthroplasty. 2016 Dec 14). These include death, infection, pulmonary embolus, blood clots in the leg, loosening of the device requiring revision, and so on.
- NSAID drugs, like Motrin, Aleve, Celebrex, and so on:
- The mortality rate for 60 days of use due to a GI bleed is 1 in 1,200.
- Almost one-third of patients who take these drugs for arthritis have damage to the gut.
- There is a 158–407% increase in the risk of dying from a heart attack (depending on the drug, dose, and length of time taken).
- Knee arthroscopy: 4.7% complication rate including infection, blood clot in the leg, pulmonary embolus, and anaesthetic-related issues
So conventional procedures and widely used medications can have big time complications and rates!
Reported Complication Rates for Stem Cell Procedures
To date, I think we’ve reported the most comprehensive paper on stem-cell-related complications. In more than 2,300 patients and 3,000 procedures, the total complication rate was 2.0%. Of those, four were deemed to be more serious and definitely related to the procedure by at least one independent reviewer not related to our group. Since this is out of 3.012, this is a serious-complication rate of 0.13%. Pretty small compared to the rates reported above for common orthopedic procedures.
This week we saw reported that the complication rate for the fat stem cell clinic that blinded three consecutive patients was approximately 0.01%. That seems about ten times less, despite the significant reported complications. Why? The data is an apples to oranges comparison.
For our reported data, a registry infrastructure was used where questionnaires were sent to every patient, and if they failed to respond, telephone calls were made. Based on conversations I have had with participating physicians, the stem cell outfit with the complications uses a passive system where the doctors are told to report the complications. It’s likely that pinging patients about what’s wrong can find more complications when compared to relying on a busy physician to report his or her complications.
Regrettably, the stem cell outfit that blinded these patients hasn’t published any safety data on the widespread use of fat stem cells, so there is no research to review. This is concerning.
The Risk of Stem Cell Procedures vs. Traditional Care
As you can see from the above risks, stem-cell-based orthopedic therapies have low-risk profiles when compared to conventional orthopedic procedures. Hence, when complications do occur, they are rare. However, to determine risk, efficacy is also needed as part of the calculus. So let’s look at knee replacement.
So how “good” is knee replacement compared to garden-variety physical therapy (PT)? Not great. In a recent study (video below), 3 in 4 knee-replacement candidates undergoing PT instead of surgery decided not get a knee replacement after one year. Also you need to amputate 5–6 knees to find just one patient who reports more than a 15% functional improvement as a result of this maximally invasive surgery.
Looking at the relative efficacy of two procedures is hard without a head-to-head comparison trial. However, in the case of knee arthritis, we can compare two different studies that both compare to PT. In the above case of knee replacement, we know how that invasive procedure fared, and below we’ll look at a same-day stem cell procedure.
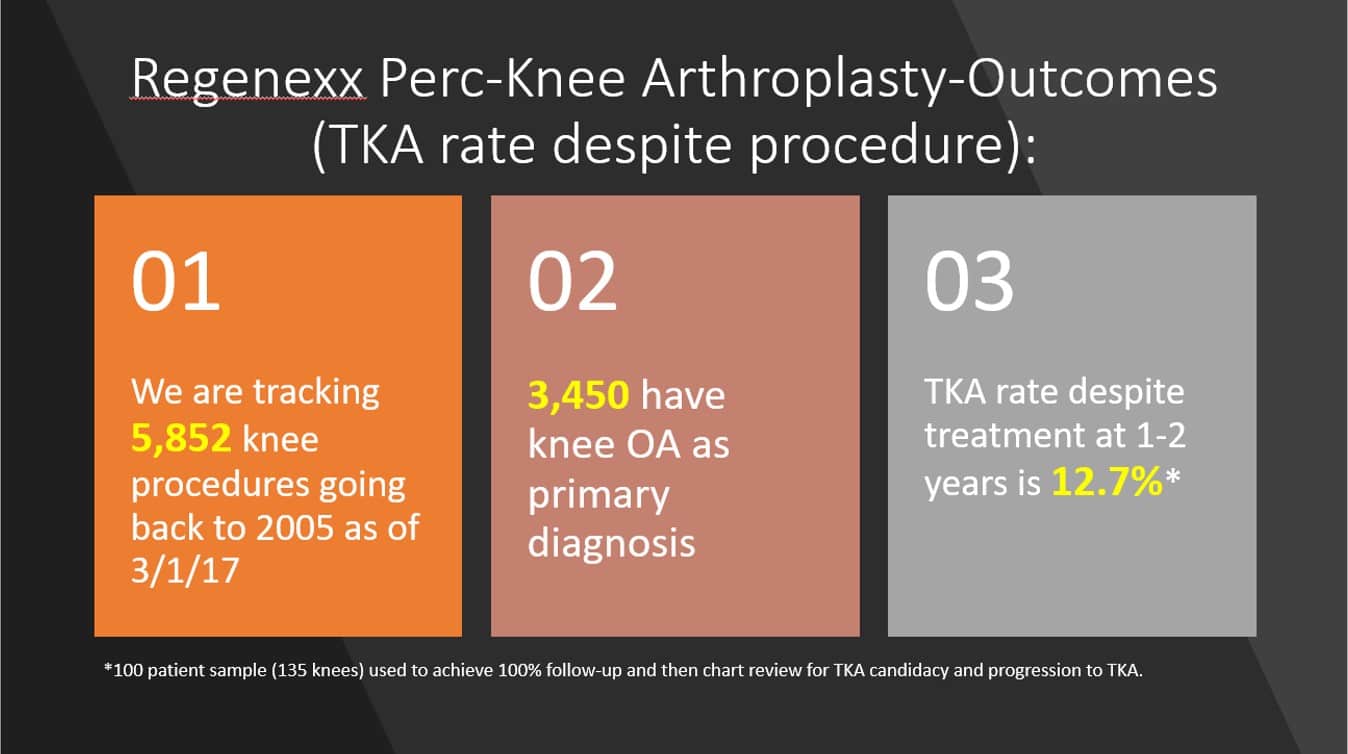
For the stem cell procedure, we’ll be looking at the Regenexx bone-marrow-based version. Below is a graphic that discusses that out of more than 5,000 knee stem-cell-treated patients, as of this month, only about 12% went on to get a knee replacement despite their treatment at 1–2 years. This was based on 100% response rate from a random sample of 100 registry patients.
Below are the yet unpublished results of our randomized controlled trial where knee-replacement candidates were treated with our Regenexx knee stem cell procedure versus physical therapy:
The patients with a stem cell procedure report more knee function more quickly compared to the physical therapy group (listed here as “Exercise Therapy”). The PT group crossed over to the stem cell procedure at three months, which is why the PT data is only tracked for that long.
So comparing risks and benefits of these two therapies, the risk of knee replacement is significantly greater and the outcome based on a randomized controlled trial is likely no better than a stem cell injection. Hence, the risk/benefit of a Regenexx-protocol knee stem cell procedure is good compared to traditional care.
The upshot? While the risks of stem cell therapy are likely lower than most traditional treatments, for some indications, like injecting fat stem cells in the eye, that equation goes in the wrong direction. The goal with today’s review was also to open a debate about when stem cell therapy is likely the better option. So let’s have a reasonable discussion about stem cell risks and not throw the baby out with the bathwater!

If you have questions or comments about this blog post, please email us at [email protected]
NOTE: This blog post provides general information to help the reader better understand regenerative medicine, musculoskeletal health, and related subjects. All content provided in this blog, website, or any linked materials, including text, graphics, images, patient profiles, outcomes, and information, are not intended and should not be considered or used as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please always consult with a professional and certified healthcare provider to discuss if a treatment is right for you.